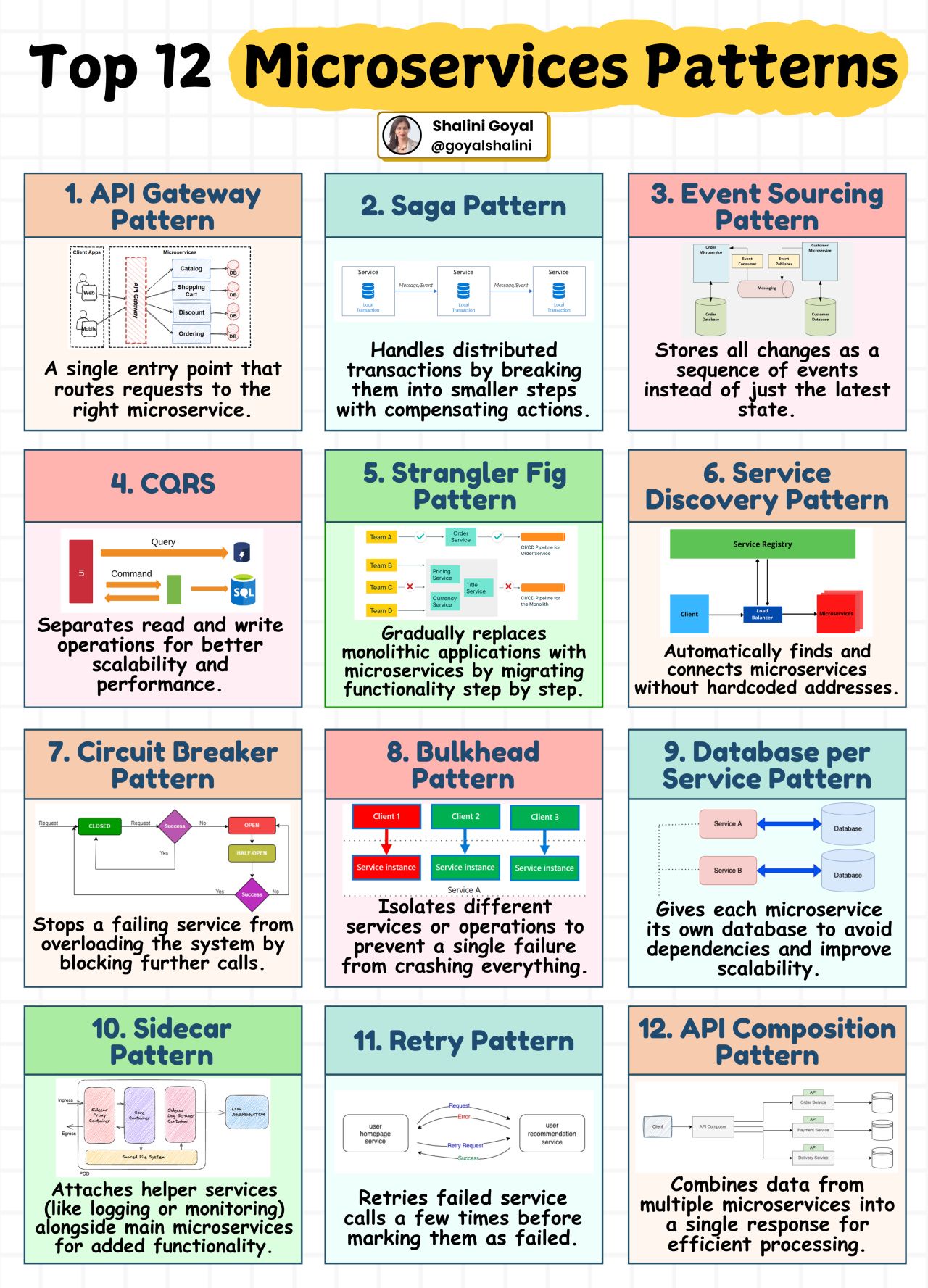
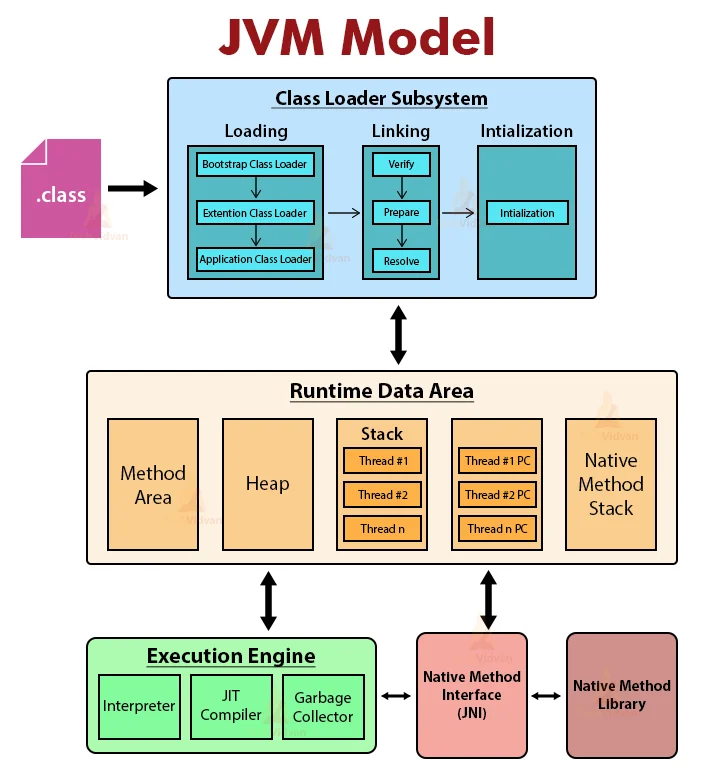
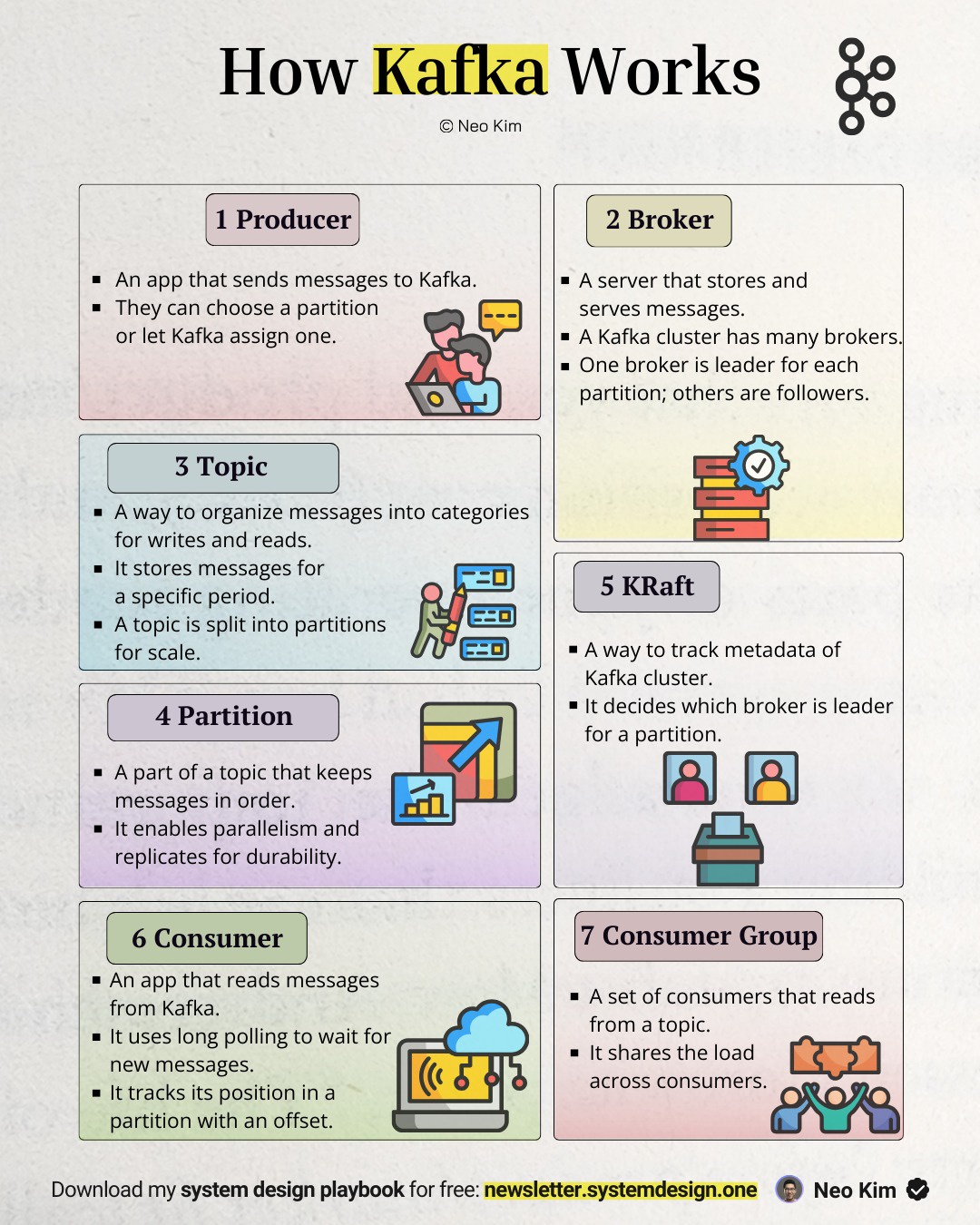
JVM Model
How Kafka Works
SOLID Principles
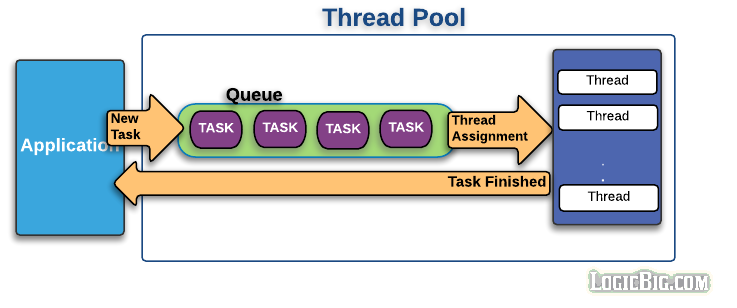
Java Thread Pool
A thread pool is the collection of pre-instantiated standby threads which are ready to execute application level tasks.
Why thread pools are important?
Thread pools improve performance by running multiple tasks simultaneously, and at the same time they prevent the time and memory overhead incur during thread creation.
For example a web server instantiates thread pool at the start up so that it won't be spending time creating threads when client requests come in.
As compared to creating thread per task, thread pools avoid running out of resources (processors, cores, memory etc) by avoiding unlimited thread creation at a time. After creating certain number of threads, they typically put the extra tasks in a waiting queue till a thread is available for a new task.
Let's understand the general concepts of thread pool before we go to the thread pool implementation in Java Executor framework.
Number of threads (N)
This is the number of threads (N) instances currently in the pool. This number gradually increases as more task are submitted to the pool.
Threads are usually created on demand as response to the new tasks submission to the pool. Total number of the threads is equal to the currently active threads plus the idle threads. Idle threads are the one which are done executing the assigned task and are not currently active. A task will be eventually assigned again to an idle thread or the idle thread might be removed from the pool if it remains inactive for a long time.
Note that a configuration parameter can be set to pre-initialized specified number of threads beforehand instead of creating them on demand.
Core pool size ©
This configuration parameter defines how many threads can at most be created per pool for the incoming tasks before the new tasks go to the queue.
This number can be fixed if the application knows beforehand that how many task will be submitted at a time. It basically a way to avoid creating too many threads and to avoid the application failure due to a lot of hardware resource consumption. The application can also adapt a runtime strategy to dynamically change this limit, depending on how many processors/core are currently available and how much memory is available for the application.
Queuing
At some point, if new task submission exceeds core pool size © then a queue is used for the extra tasks.
If total tasks submitted to the pool are T, and C of them are currently being executed by the threads then remaining tasks (T-C, assuming T>C) have to wait in the queue for the currently running tasks to finish and take their places one by one.
Bounded vs Unbounded queues
Queues can be bounded (having a predefined capacity) or unbounded (without a predefined capacity).
What happens if number of queued tasks exceeds beyond the capacity of a bounded queue?There might be two logical approaches there: either extra tasks should be rejected at this point or new threads should be allowed to be created again. Now if new threads are allowed again then unlimited task submission may again bring about the resource crisis and eventually application might fail. Well at least Java provides a solution to that problem (We will see Java implementation shortly in following sections), the solution is to provide another limiting parameter, known as pool maximum size (M) for the new threads creation. Once this limit is reached, more task submission will be rejected for thread assignment.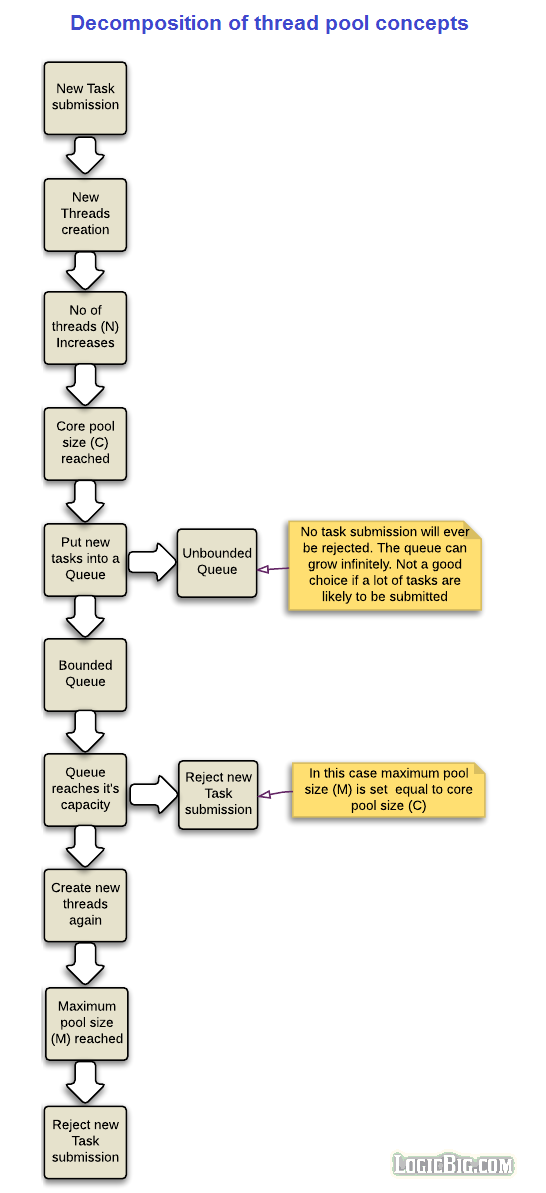
Maximum pool size (M)
This is the maximum number of threads instances created for the submitted tasks. This can dynamically be changed by the application.
No effect of M when using unbounded queues
An unbounded queue will grow infinitely without reaching the point to consider maximum pool size (M). That means the value of the M doesn't have any effect in that case. A task will never be rejected in the unbounded queue.
Trade off between M and bounded queues
Using high capacity bounded queues and small number of core threads © minimizes CPU usage, OS resources, and context-switching overhead, but will yield low throughput.
Use of low capacity bounded queues generally requires larger pool sizes, which increases CPUs usage. In this case if threads use shared data then probably we have to use locks which also decreases throughput.
Idle threads
After it's creation and running one or more tasks, a thread can become idle if it's not currently engaged in running a task. Depending on the application requirements, if a thread is idle for a long time, it's better to remove it from the pool to reclaim resources. A thread pool implementation should provide configuration parameters to specify whether idle threads should be removed from the pool or not and also what should be the timeout for the removal.
Java Thread Pool implementations
ThreadPoolExecutor class
This class provides a very versatile implementation to create wide range of thread pools with the help of supplied parameters at constructions time. The most of those parameters can be changed dynamically as well.
Let's examine the different constructors of this class:
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
corePoolSize :
Same as C as described above.
For N <= C (corePoolSize) , the idle threads are not assigned the new incoming task, instead new threads are created.
For N > C (corePoolSize) and if there are some idle threads then new task is assigned there, otherwise they are put into the queue.
getPoolSize() gives current value of N.
getCorePoolSize() gives the value of C (corePoolSize).
This value may also be changed dynamically by using setCorePoolSize(int)
maximumPoolSize:
Same as M described above.
This value can be changed dynamically by using setMaximumPoolSize(int corePoolSize)
keepAliveTime:
When N > C (corePoolSize) then idle threads are monitored for how long they have been idle. On crossing keepAliveTime, idle threads are terminated (removed from the pool).
The method allowCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean) can be used to apply this timeout policy to core threads as well.
This parameter provides a means of reducing resource consumption when the pool is not being actively used. If the pool becomes more active again later, new threads will be constructed.
Value of Long.MAX_VALUE TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS effectively disables idle threads from ever terminating prior to shut down.
There's a setter for this property too: setKeepAliveTime(long time, TimeUnit unit)
unit:
the time unit for the keepAliveTime parameter.
workQueue
The queue instance which has to be BlockingQueue.
As mentioned above queues can be bounded (e.g. ArrayBlockingQueue) or it can be unbounded (e.g. LinkedBlockingQueue).
There's a third option, i.e. use direct hand-offs queue e.g. SynchronousQueue which immediately attempts to assign a task to an available thread. If no thread is available because maximum pool size (M) has been reached, then task will be rejected. There's no much meaning with corePoolSize © with this option e.g. if corePoolSize = 2 and maximumPoolSize = 5 then queue Size will always return 0 because the task is never held in the queue. getCorePoolSize() will always return 2 but it doesn't have any effect. After reaching 5 (the maximum limit) the new task will be reject.
We are free to use any implementation of the blocking queue, whatever is suitable for our need. Please explore all possible queue implementations here
handler
An instance of RejectedExecutionHandler to use when the tasks are submitted beyond the pool maximum size. This handler takes care of what action needs to be taken for new tasks submissions at this point.
RejectedExecutionHandler interface:
package java.util.concurrent;
public interface RejectedExecutionHandler {
void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor);
}
Besides providing our own instance of this interface, ThreadPoolExecutor provides four out of the box nested implementation to be used:
- ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy: This is the default rejection policy. It throws RejectedExecutionException:
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}
- ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy: Instead of rejecting the task, it is attempted to run in the caller thread:
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}
Using this will obviously slow down the rate that new tasks are submitted. * ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy: The task is quietly rejected:
public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
}
- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy: It removes the oldest task in the queue and executes the new one right away instead of rejecting it:
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
}
threadFactory
This parameter provides a factory of java.lang.Thread creation for the pool. This interface has only one method as shown:
package java.util.concurrent;
public interface ThreadFactory {
Thread newThread(Runnable var1);
}
If not used, Executors.defaultThreadFactory() is used which creates all threads having NORM_PRIORITY, are non-daemon and belong to the same ThreadGroup.
Other useful methods
int prestartAllCoreThreads()
Calling this method overrides the default policy of on-demand creation of thread instances. The threads start in idle mode and wait for the task assignment. This method returns number of threads which actually started.
Calling boolean prestartCoreThread() will start only one thread. This method returns false if all core threads have already been started
Example
Let's see how different queues work with ThreadPoolExecutor:
public class ThreadPoolExecutorExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
createAndRunPoolForQueue(new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), "Bounded");
createAndRunPoolForQueue(new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(), "Unbounded");
createAndRunPoolForQueue(new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), "Direct hand-off");
}
private static void createAndRunPoolForQueue (BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue,
String msg) {
System.out.println("---- " + msg + " queue instance = " +
queue.getClass()+ " -------------");
ThreadPoolExecutor e = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, Long.MAX_VALUE,
TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS, queue);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
e.execute(new Task());
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
System.out.println("Task rejected = " + (i + 1));
}
printStatus(i + 1, e);
}
e.shutdownNow();
System.out.println("--------------------\n");
}
private static void printStatus (int taskSubmitted, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("poolSize = ")
.append(e.getPoolSize())
.append(", corePoolSize = ")
.append(e.getCorePoolSize())
.append(", queueSize = ")
.append(e.getQueue()
.size())
.append(", queueRemainingCapacity = ")
.append(e.getQueue()
.remainingCapacity())
.append(", maximumPoolSize = ")
.append(e.getMaximumPoolSize())
.append(", totalTasksSubmitted = ")
.append(taskSubmitted);
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
private static class Task implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run () {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}