APIGateway
AIRBNB'S Evolution
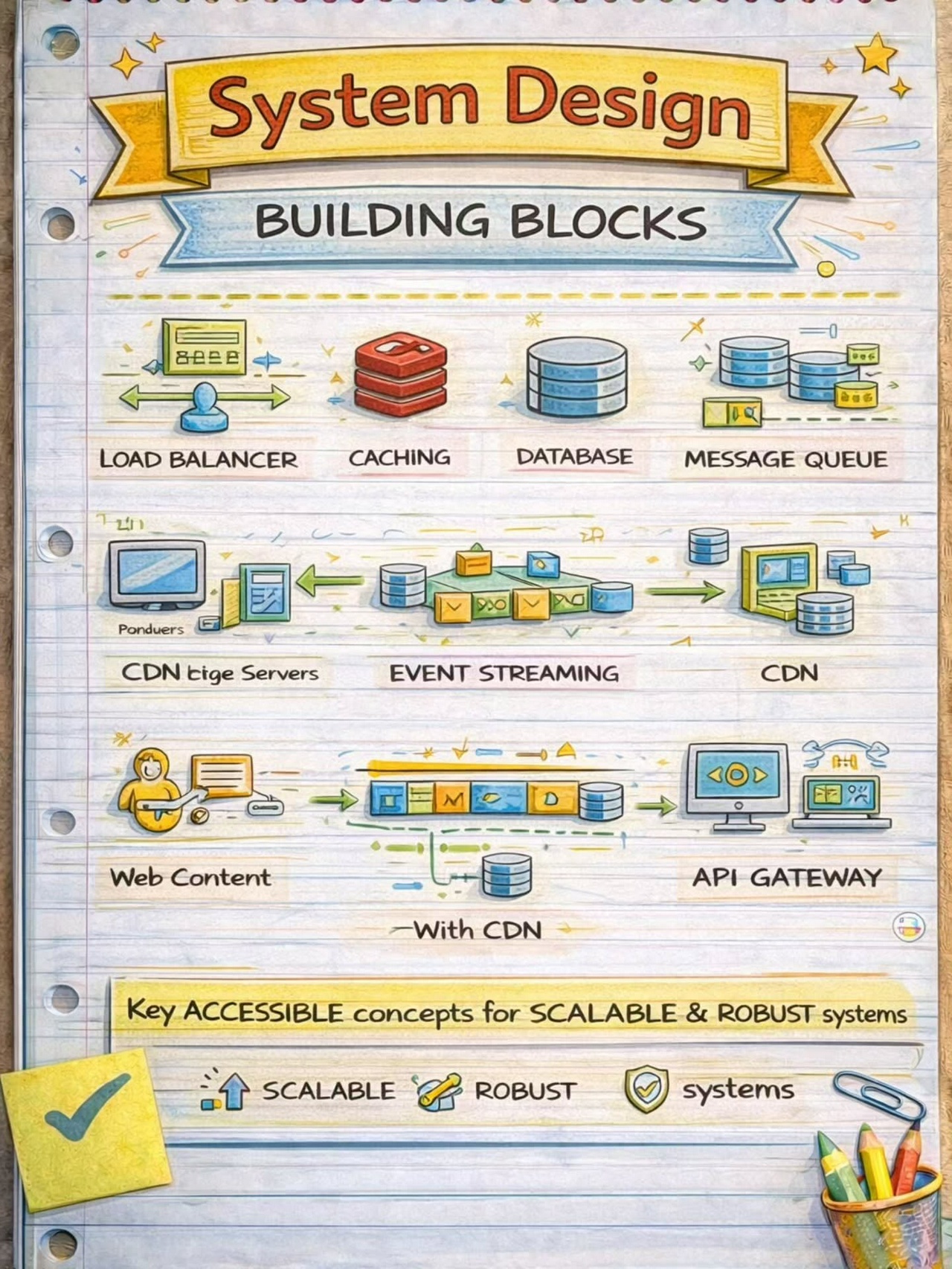
Top 9 System Integrations

Top 9 Architectural Patterns for Data and Communication Flow
Peer-to-Peer
The Peer-to-Peer pattern involves direct communication between two components without the need for a central coordinator.
API Gateway
An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for all client requests to the backend services of an application.
Pub-Sub
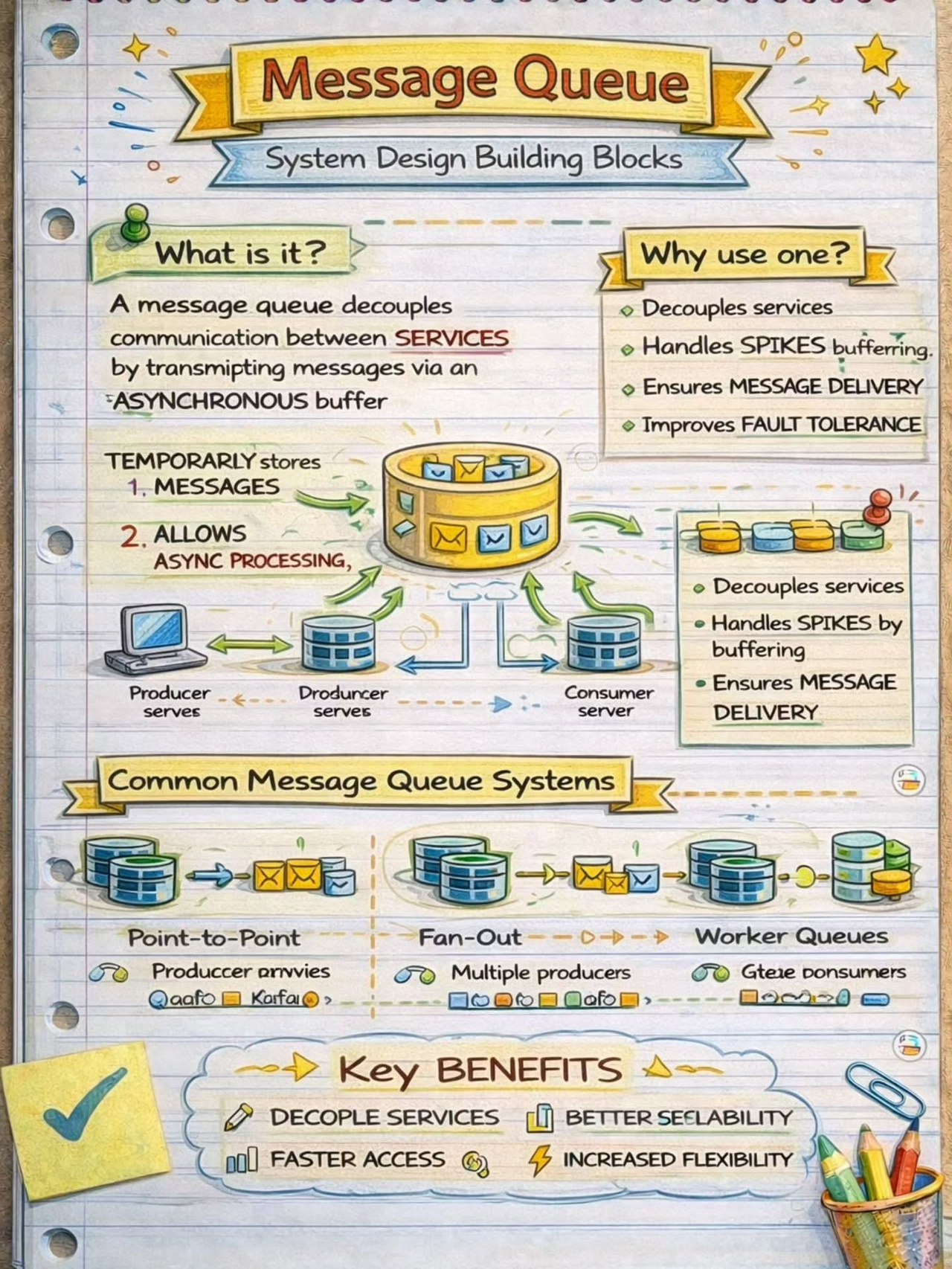
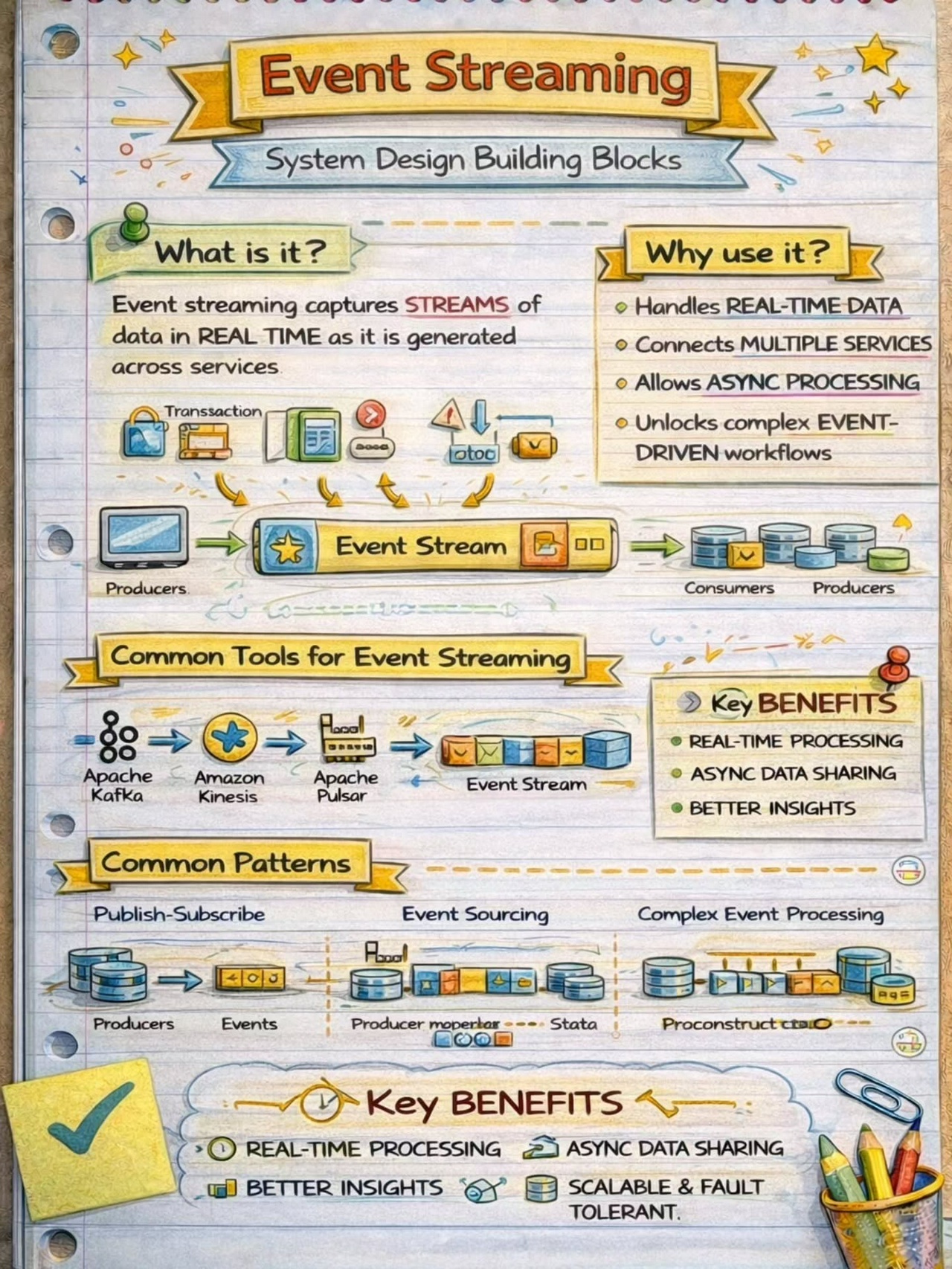
The Pub-Sub pattern decouples the producers of messages (publishers) from the consumers of messages (subscribers) through a message broker.
Request-Response
This is one of the most fundamental integration patterns, where a client sends a request to a server and waits for a response.
Event Sourcing
Event Sourcing involves storing the state changes of an application as a sequence of events.
ETL
ETL is a data integration pattern used to gather data from multiple sources, transform it into a structured format, and load it into a destination database.
Batching
Batching involves accumulating data over a period or until a certain threshold is met before processing it as a single group.
Streaming Processing
Streaming Processing allows for the continuous ingestion, processing, and analysis of data streams in real-time.
Orchestration
Orchestration involves a central coordinator (an orchestrator) managing the interactions between distributed components or services to achieve a workflow or business process.
#SystemIntegrations #APIGateway #PubSub #Batching #ETL #RequestResponse
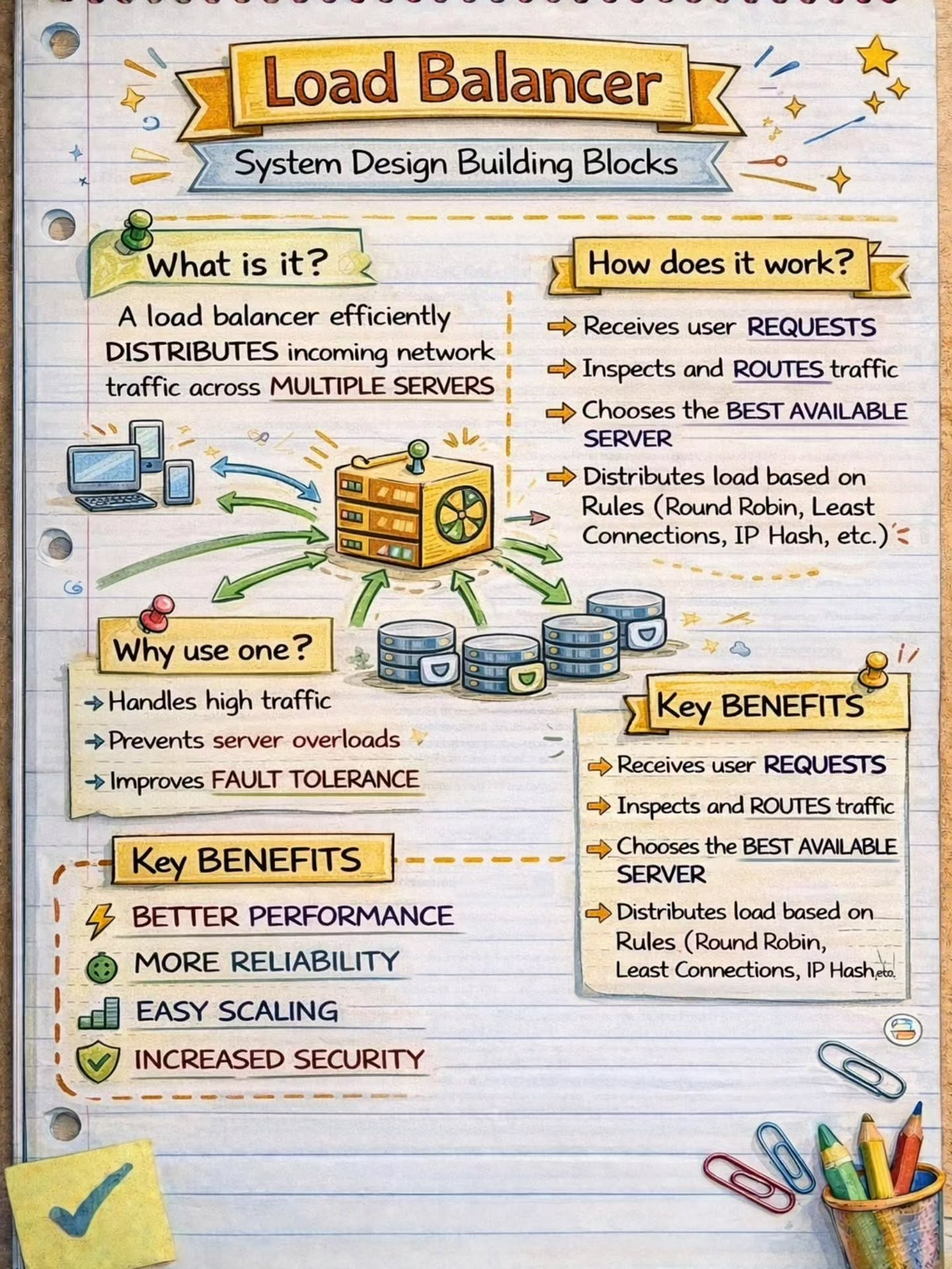
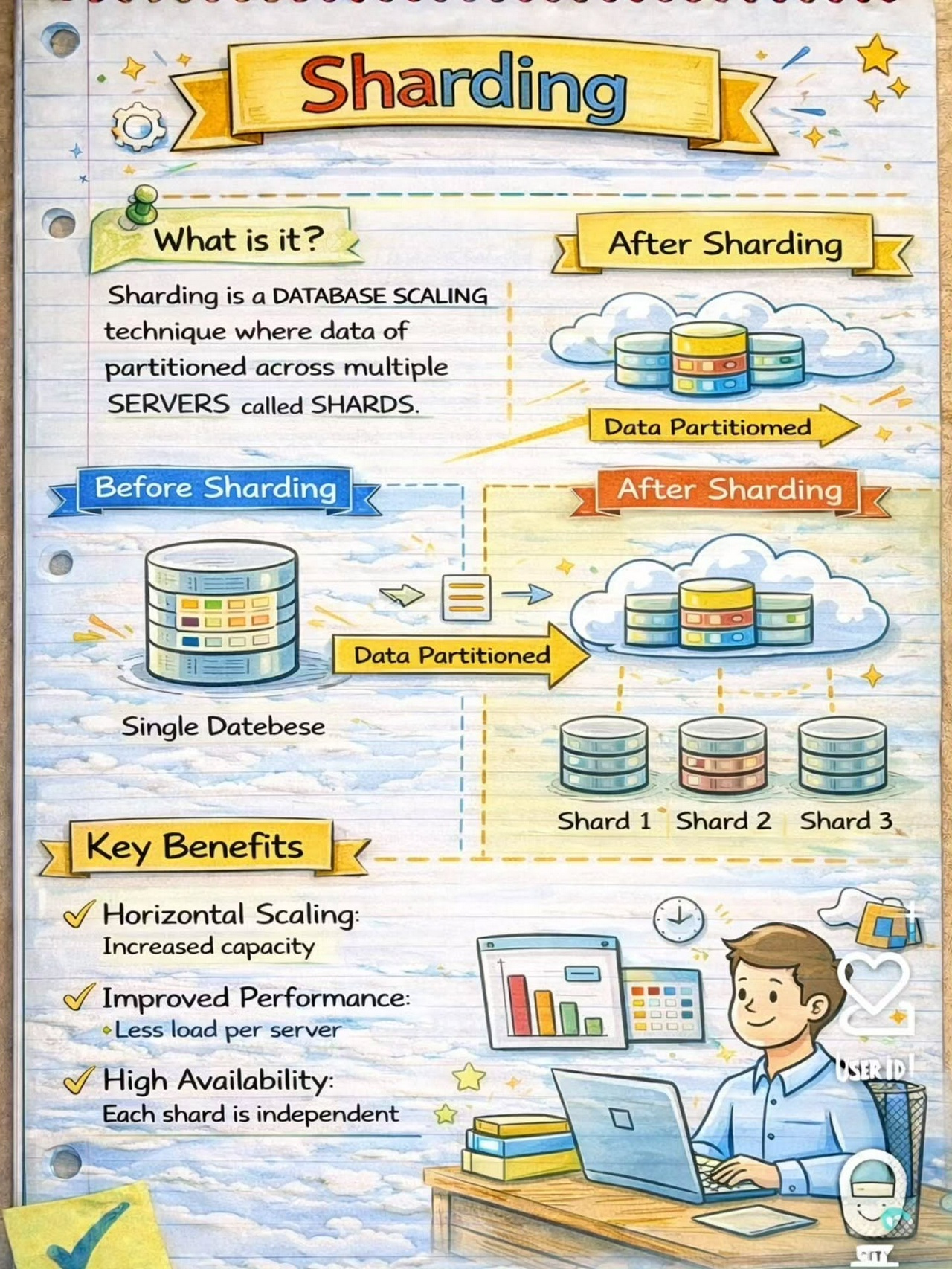
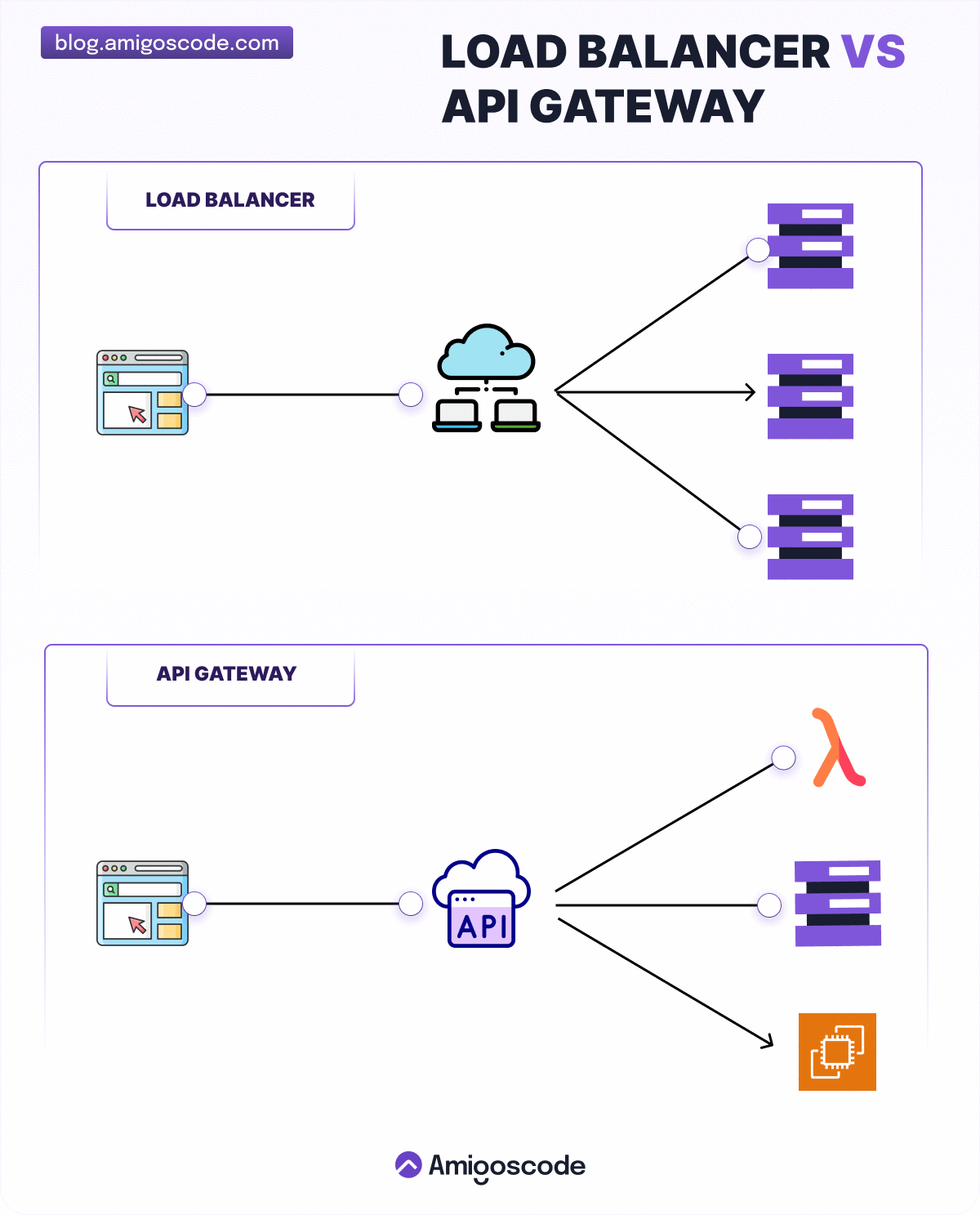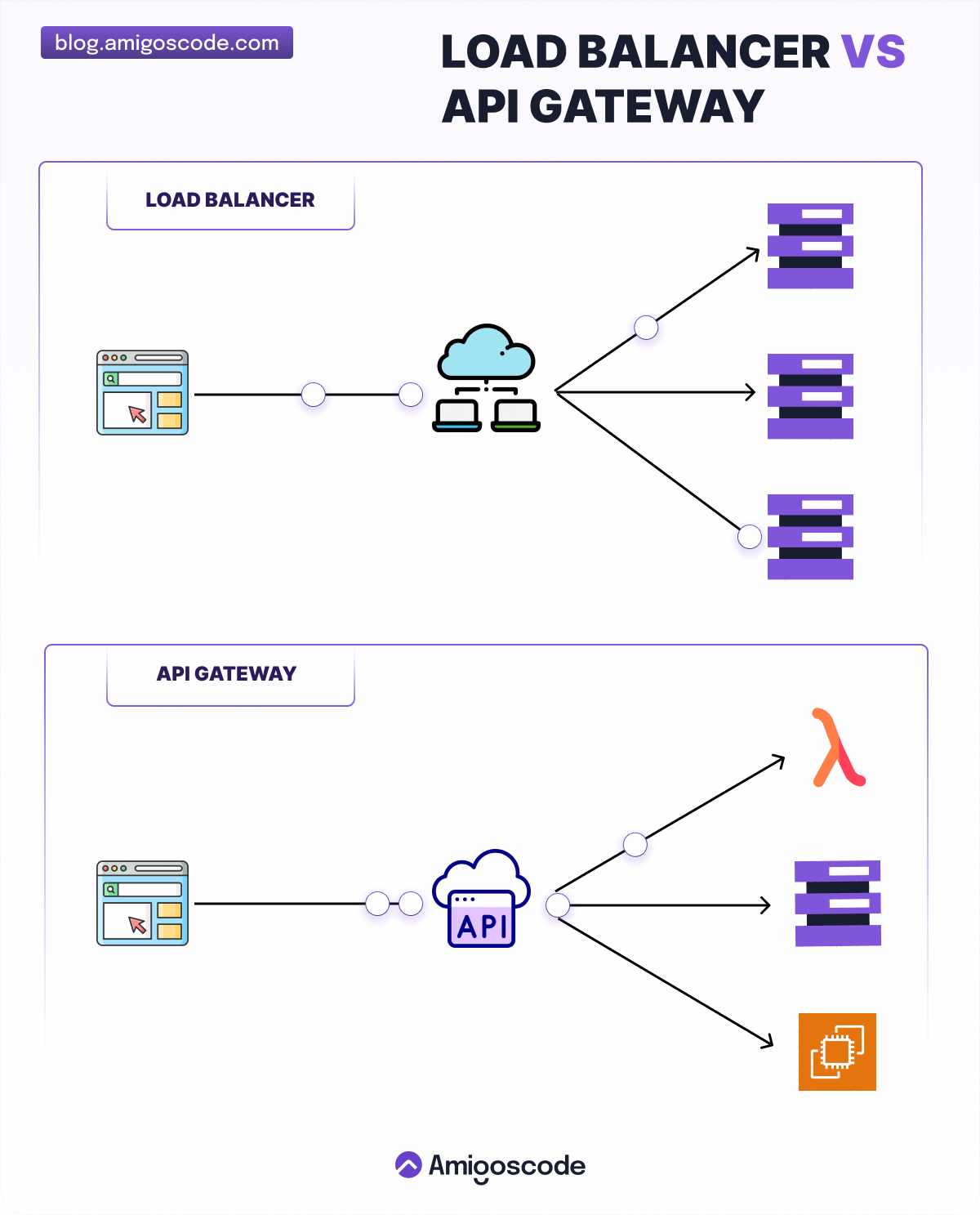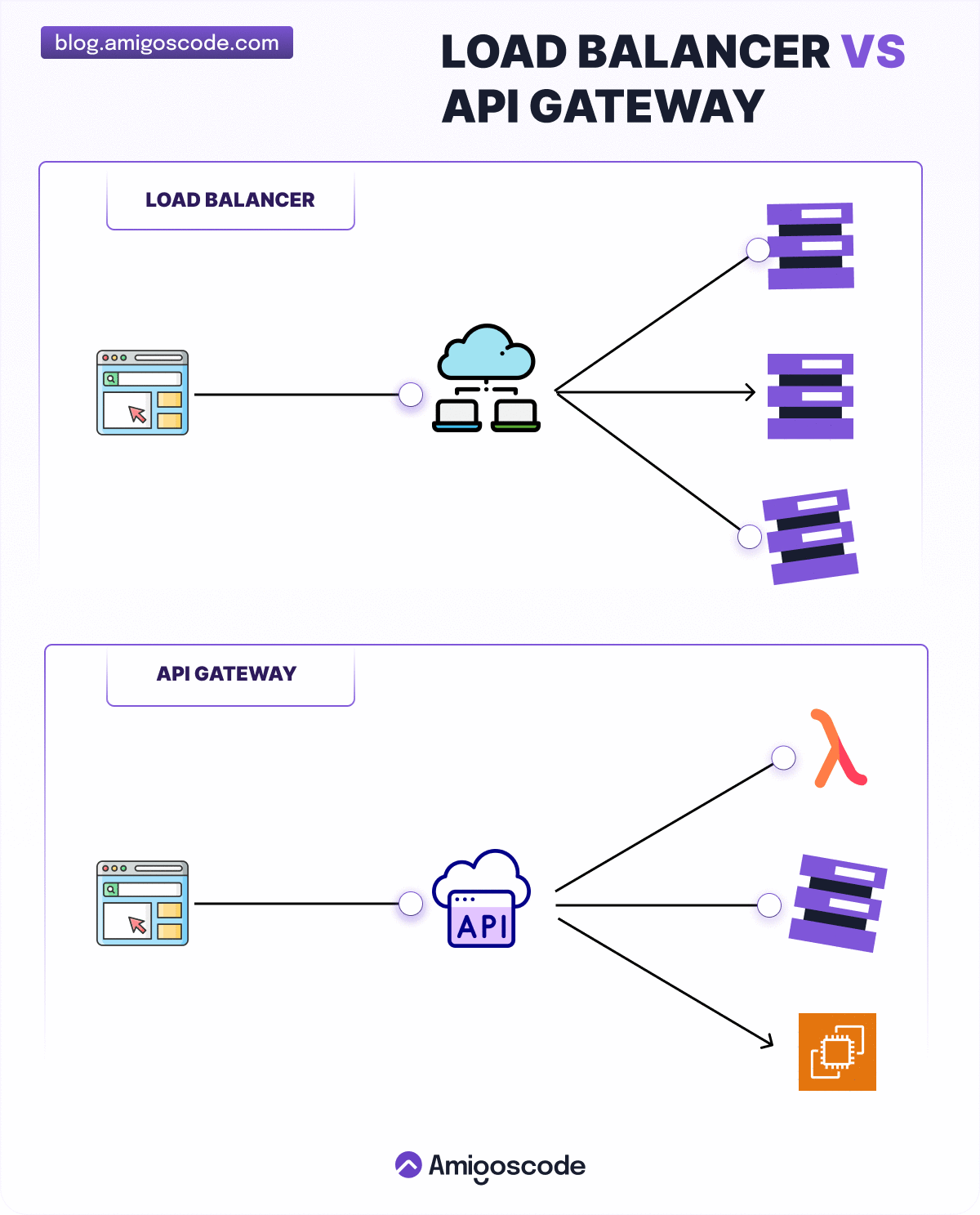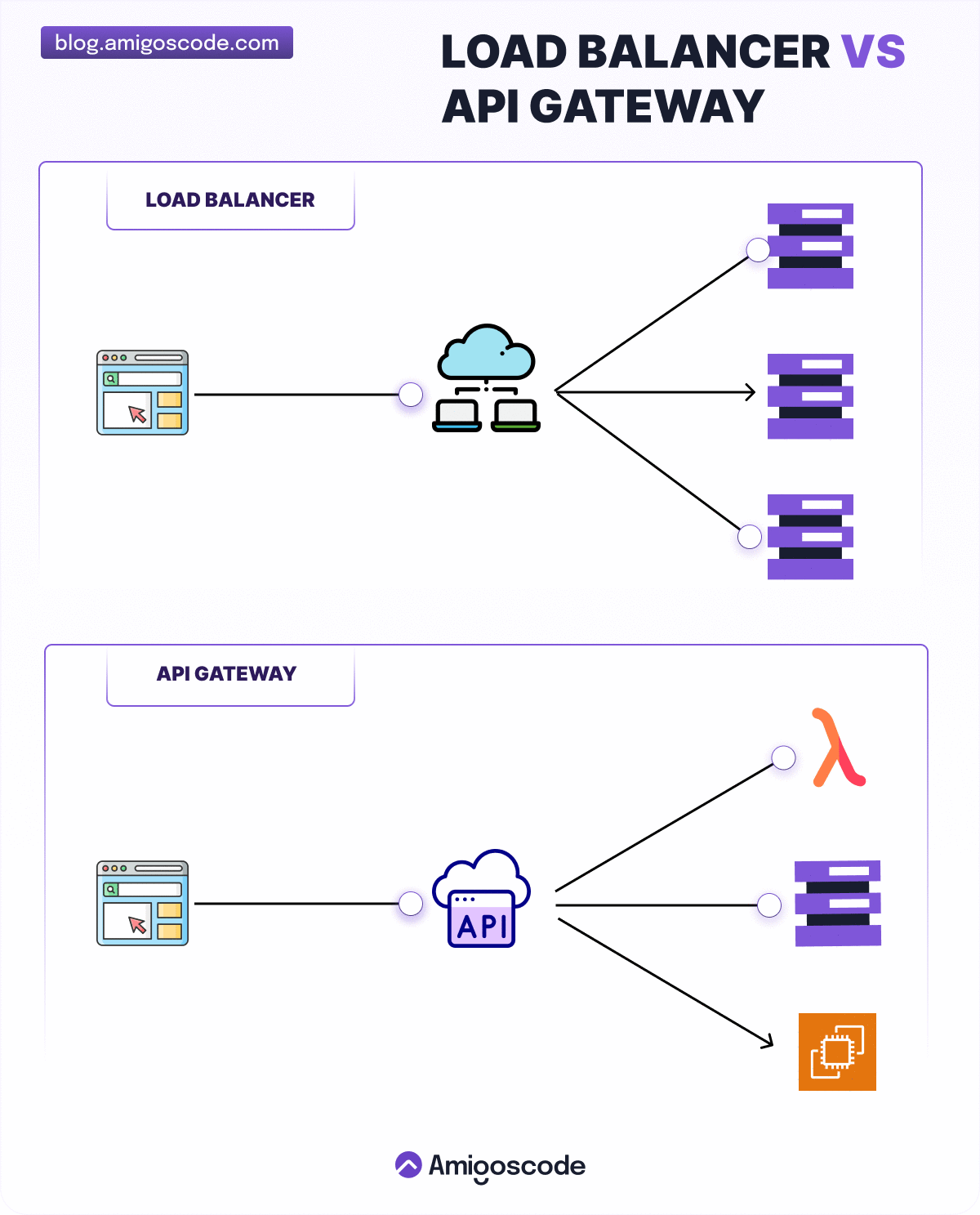
Load Balancing
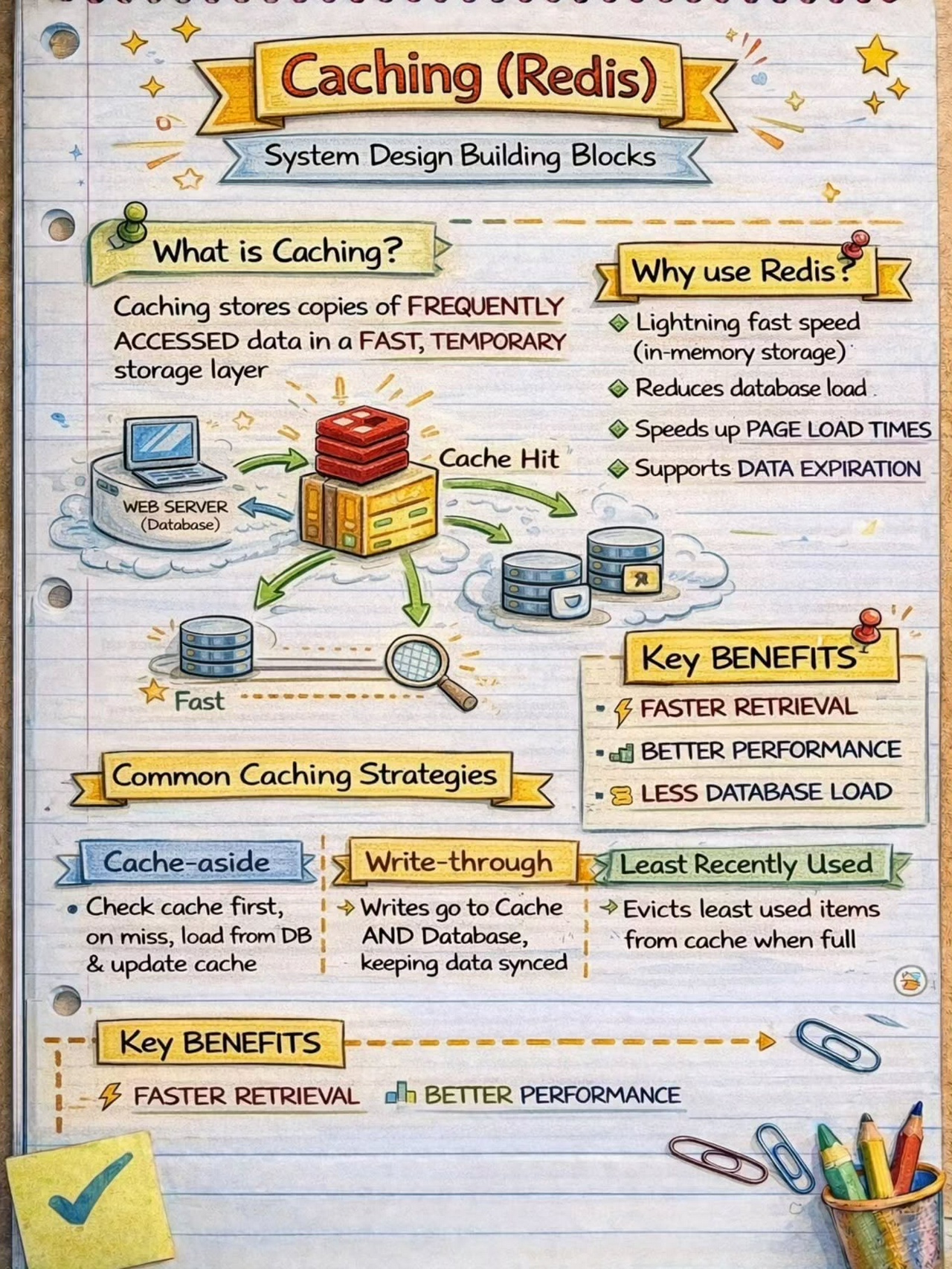
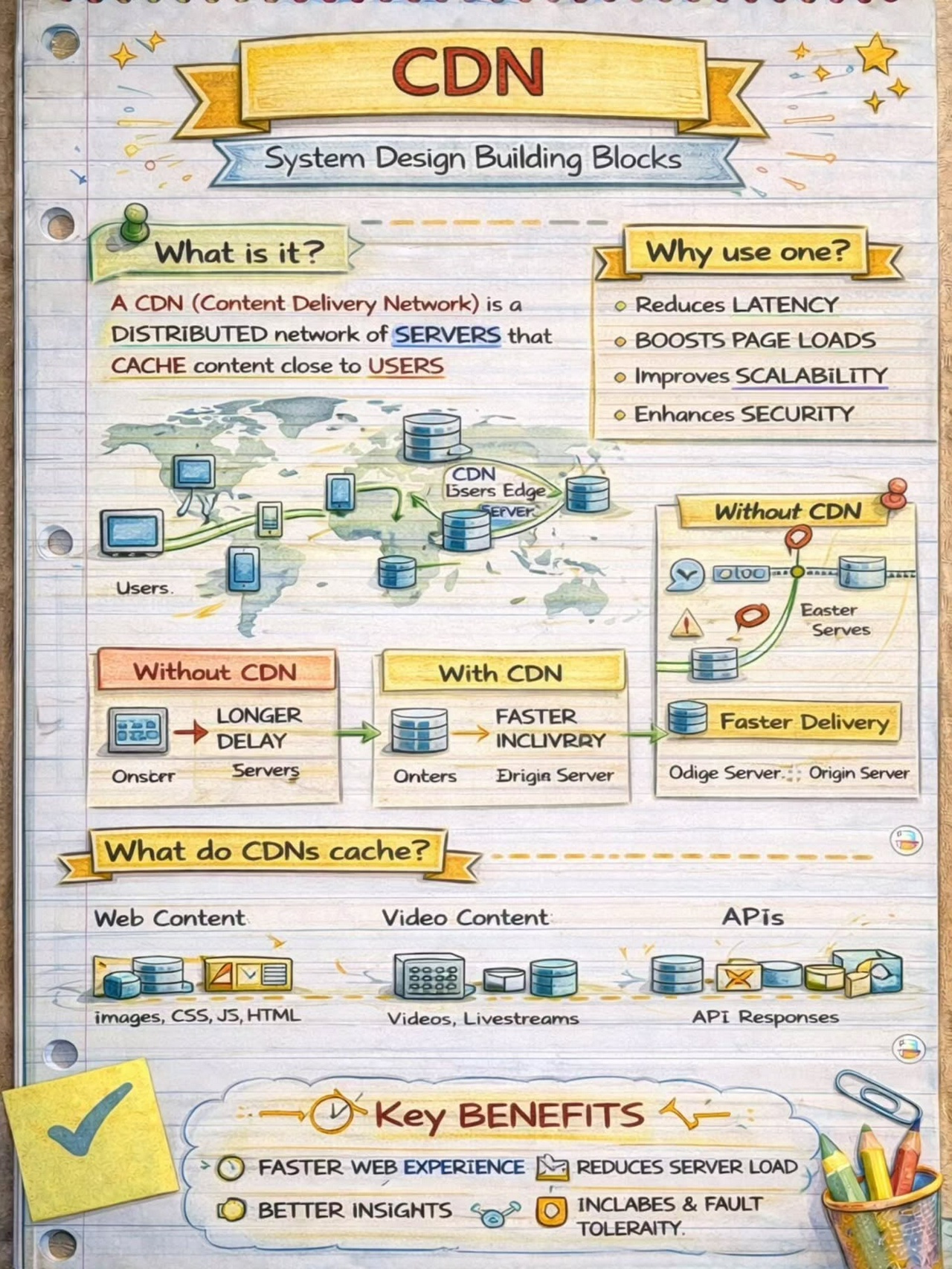
Where is Data Cached?
API Gateway in Detail
API Gateways are essential components in modern software architectures, particularly microservices-based systems.
They act as a single entry point for all API requests, providing a unified interface for accessing various services and data. By decoupling client applications from backend microservices, API Gateways simplify API management and enhance the overall performance and security of the system.
API Gateways help enhance the developer experience while building scalable and maintainable systems. Organizations can achieve better control over their API landscape by using API Gateways.
As the complexity of software systems continues to grow, API Gateways will play an increasingly important role in enabling effective communication and integration between services and clients.
In this post, we’ll explore the various aspects of API Gateways in detail.

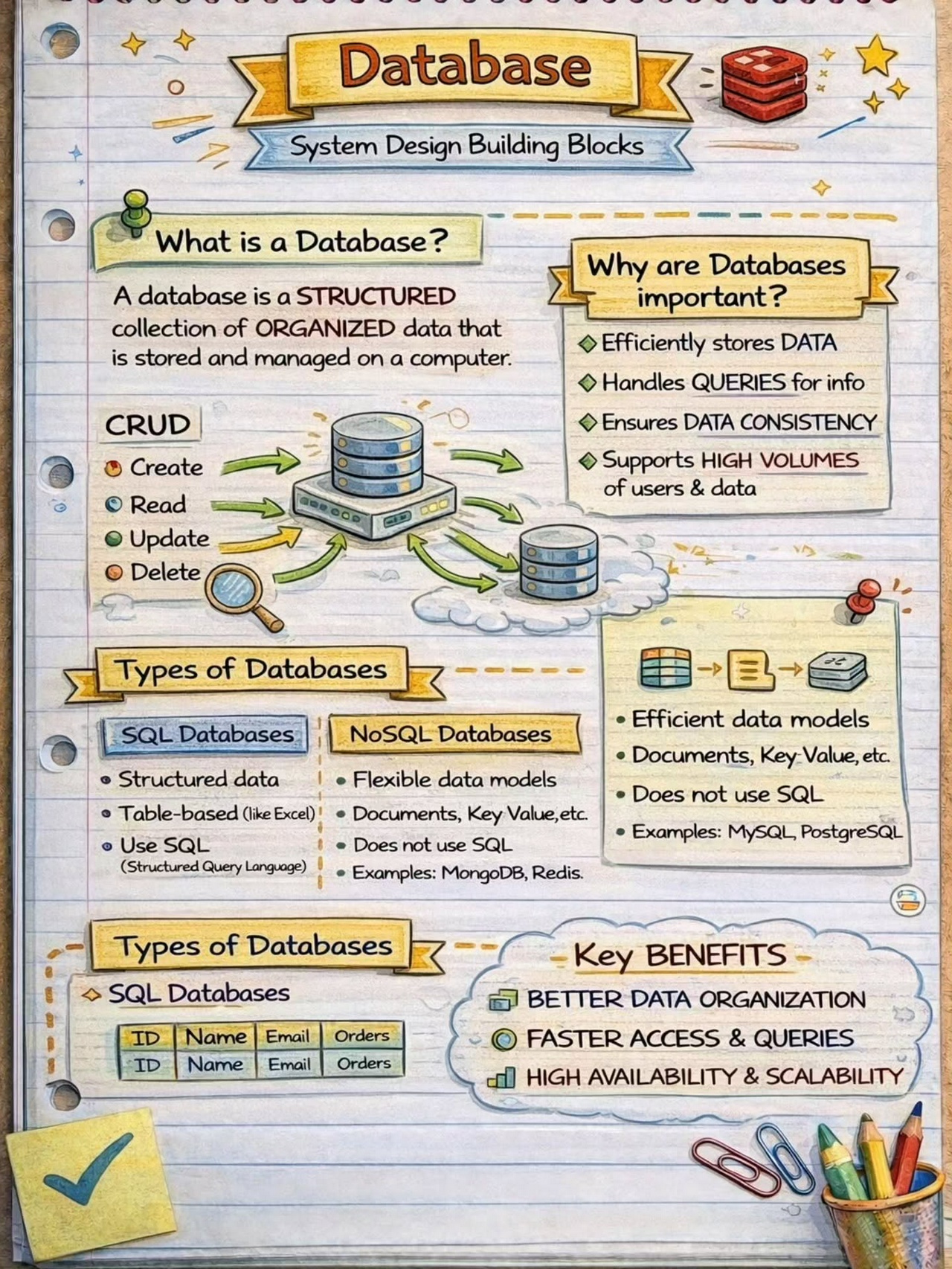
What is an API Gateway
An API Gateway is a component that serves as the central entry point for all API requests in a system.
Its primary purpose is to decouple the client applications from the backend microservices, providing a consistent and unified interface for accessing different services and data sources.

Implementing an API Gateway offers several key benefits such as:
- Centralized API Management: API Gateways simplify the management of APIs by providing a central location for routing, monitoring, and securing API traffic. This centralization makes enforcing policies, tracking usage, and troubleshooting issues easier.
- Improved Security: By enforcing security policies, such as authentication and authorization, at a central point, API Gateways protect backend services from unauthorized access. They act as a security layer, ensuring only authenticated and authorized clients can interact with the underlying services.
- Enhanced Performance: API Gateways can improve the performance and scalability of API services by implementing caching, rate limiting, and load balancing. Caching frequently accessed data at the gateway level reduces the load on backend services, while rate limiting prevents abuse and ensures fair usage of resources. Load balancing distributes incoming requests across multiple instances of a service, improving overall performance and reliability.
- Simplified Client Interaction: API Gateways provide a consistent and simplified interface for client applications, regardless of the complexity of the underlying microservices architecture. This simplification reduces the complexity of client development and makes it easier to consume APIs.
Key Features and Functionalities of API Gateways
API Gateways offer a wide range of functionalities that simplify API management, enhance security, and improve the overall performance and scalability of the system.
The diagram below shows the various features that API Gateways can support.

Let's now explore some key functionalities provided by API Gateways.
Request Routing and API Composition
One of the primary functions of API Gateways is request routing.
They act as a single entry point for client requests and intelligently route them to the appropriate backend services based on the request parameters, headers, or other criteria. This centralized routing mechanism simplifies client development and allows for flexible scaling and deployment of backend services.
API Gateways also support API composition, which involves aggregating and combining multiple API calls into a single request. This capability reduces the number of round trips between the client and the backend, improving performance and reducing network overhead.
API Gateways can also perform request transformation, modifying headers, query parameters, or payloads before forwarding the request to the backend services, ensuring compatibility and consistency.
Protocol Transformation and Translation
API Gateways support multiple communication protocols, such as HTTP, WebSocket, and gRPC, and can seamlessly translate between them. This protocol transformation capability allows clients and backend services to use different protocols while the API Gateway handles the necessary translations.
Additionally, API Gateways can convert the request and response formats, such as JSON to XML or vice versa, based on the client's requirements or the backend service's expectations. They can also handle protocol-specific features, such as HTTP method override or content negotiation, providing flexibility and interoperability.
API Versioning and Lifecycle Management
API Gateways play a crucial role in API versioning and lifecycle management.
They enable the coexistence of multiple versions of an API, allowing developers to introduce new features or make changes without disrupting existing clients. API Gateways can route requests to the appropriate version of the backend service based on the version specified in the request.
Moreover, API Gateways facilitate API lifecycle management, including deprecating older versions, providing migration paths, and handling version-specific configurations. This functionality ensures a smooth transition for clients as APIs evolve.
Authentication and Authorization
Security is critical for API management, and API Gateways provide robust authentication and authorization mechanisms.
They handle the authentication of client requests before forwarding them to the backend services, supporting various authentication schemes such as API keys, OAuth tokens, or JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
API Gateways validate and verify the authentication credentials, ensuring that only authorized clients can access protected resources. They can also enforce fine-grained authorization rules based on user roles, permissions, or other attributes, providing granular access control and security.
Rate Limiting and Throttling
To protect backend services from excessive traffic and ensure fair usage, API Gateways implement rate limiting and throttling.
They can limit the number of requests per client, API key, or IP address within a specific time window, preventing abuse and mitigating the impact of high-traffic scenarios.
API Gateways can also implement burst limits, allowing clients to temporarily exceed the rate limit for a short period. Throttling helps maintain the overall performance and availability of the API by regulating the incoming traffic.
Caching and Response Caching
Caching is a powerful technique to optimize performance and reduce the load on backend services. API Gateways can cache frequently accessed data or API responses at various levels, such as per client, per API, or per resource.
By serving cached responses, API Gateways can reduce response times and minimize the impact of high-traffic scenarios. They can also invalidate cached data based on predefined rules or when the underlying data changes, ensuring data consistency.
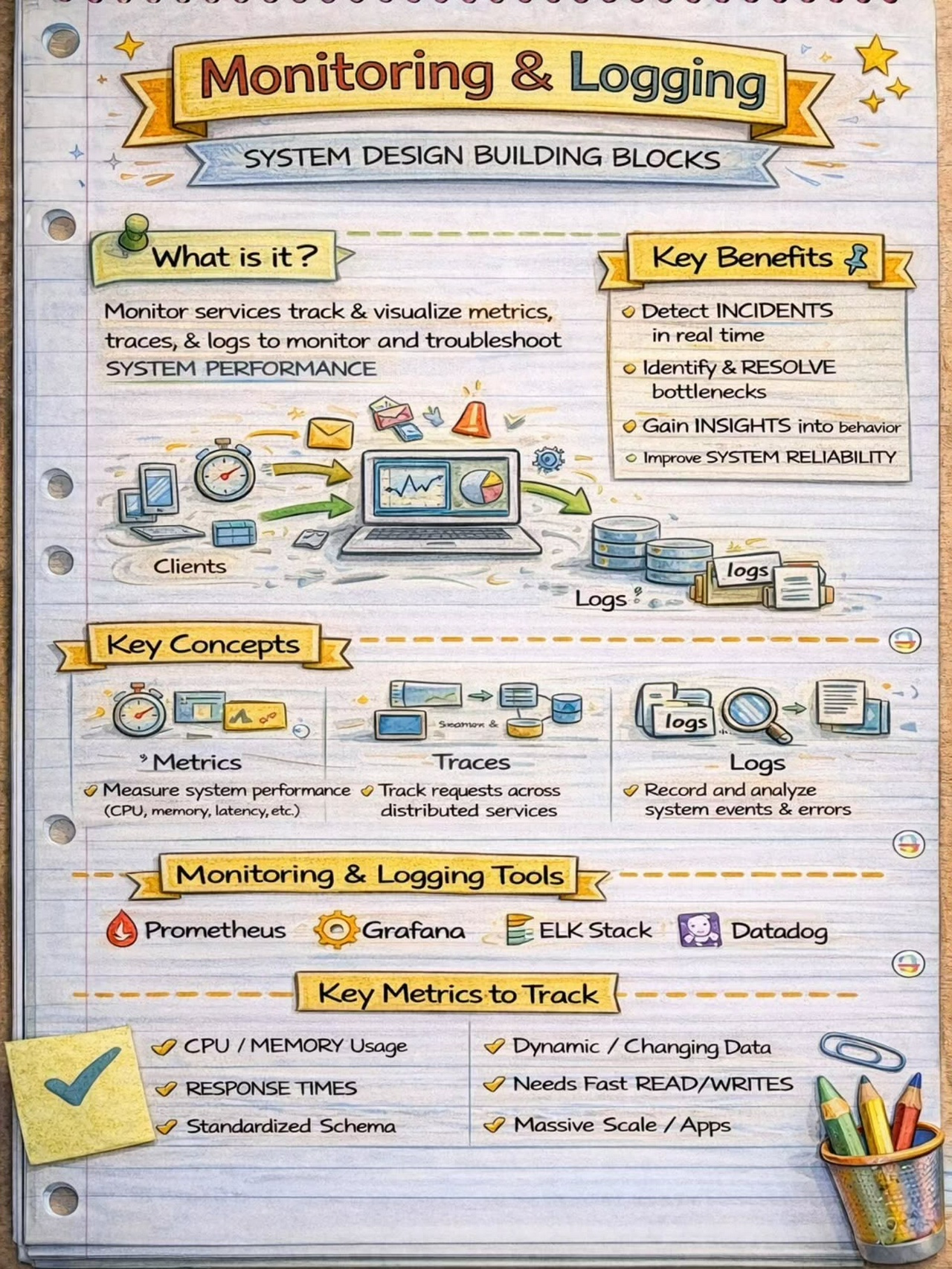
Logging, Monitoring, and Analytics
API Gateways provide comprehensive logging and monitoring capabilities to track API usage, performance, and errors. They can log request and response metadata, such as headers, payloads, and response times, enabling detailed analysis and troubleshooting.
Integration with monitoring and analytics tools allows API Gateways to provide valuable insights into API usage patterns, identify bottlenecks, and monitor the overall health and performance of the API ecosystem. Real-time metrics and dashboards facilitate proactive monitoring and timely resolution of issues.
API Gateway Architecture
Let's explore the key architectural components, design patterns, and considerations in building robust API Gateways.
Architectural Components and Design Patterns
API Gateways typically consist of several essential architectural components and follow specific design patterns to enable efficient API management and delivery.
Reverse Proxy and Gateway Routing
API Gateways act as a reverse proxy, receiving client requests and forwarding them to the appropriate backend services.
The gateway handles the routing logic and determines which service should handle each request.
Key aspects of reverse proxy and Gateway routing include:
- Dynamic Routing: API Gateways can dynamically route requests based on various factors such as URL paths, query parameters, headers, or request payload. This flexibility allows for configurable and adaptive routing rules that can be modified as needed.
- Load Balancing: API Gateways can distribute incoming requests across multiple instances of a backend service to ensure optimal performance and high availability. They can employ different load balancing algorithms like round-robin, least connections, or weighted distribution to distribute the traffic evenly.
Microservice Integration and Service Discovery
API Gateways play a vital role in integrating microservices and facilitating service discovery in a microservices architecture.
Key aspects of microservices integration and service discovery include:
- Service Registry: API Gateways often integrate with a service registry, which maintains a directory of available services and their network locations. The gateway uses this information to route requests to the appropriate services, enabling dynamic service discovery and load balancing.
- Service Orchestration: API Gateways can orchestrate and compose multiple microservices to fulfill a single client request. They can aggregate data from multiple services, perform transformations, and handle service dependencies, providing a unified and coherent API response to the client.
- Circuit Breaker and Fault Tolerance: API Gateways can implement circuit breaker patterns to handle failures and prevent cascading failures across microservices. They can detect unresponsive services, route requests to fallback services, or return cached responses to maintain system stability and resilience.
The diagram below shows the role of API Gateway in a microservice architecture.

The Role of API Gateway in Application Security
API Gateways play a crucial role in securing and protecting API communication by implementing various authentication mechanisms, enforcing authorization and access control policies, and following security best practices.
Let's explore the key aspects of API Gateway security.
Authentication Mechanisms
API Gateways support different authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of clients accessing the APIs. Some common authentication mechanisms include:
- JSON Web Tokens (JWT): JWTs are a compact and self-contained way of securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. API Gateways can validate and verify JWTs to authenticate clients and extract relevant information from the token payload.
- OAuth: OAuth is an open standard for authorization that allows clients to access protected resources on behalf of the resource owner. API Gateways can act as OAuth servers, handling the OAuth flow and issuing access tokens to authenticated clients.
- API Keys: API keys are unique identifiers that are assigned to clients to authenticate their requests. API Gateways can validate API keys and ensure that only authorized clients with valid keys can access the APIs.
- Basic Authentication: Basic authentication involves sending username and password credentials in the request headers. API Gateways can validate these credentials against a user database or identity provider.
See the diagram below on one possible approach to secure the backend with API Gateways using an identity provider.

Authorization and Access Control
Once a client is authenticated, API Gateways enforce authorization and access control policies to determine what actions or resources the client is allowed to access. Key aspects of authorization and access control include:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): API Gateways can define and enforce RBAC policies, where clients are assigned specific roles, and each role is granted permission to access certain APIs or perform specific actions.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): ABAC policies define access control based on attributes associated with the client, resource, or environment. API Gateways can evaluate these attributes to make fine-grained access control decisions.
- Scope-Based Access Control: API Gateways can limit the scope of access granted to clients based on the permissions associated with their access tokens. Scopes define the specific actions or resources a client is allowed to access.
SSL/TLS Encryption and HTTPS
To protect the confidentiality and integrity of API communication, API Gateways should enforce the use of SSL/TLS encryption and HTTPS. Key considerations include:
- SSL/TLS Certificates: API Gateways should be configured with valid SSL/TLS certificates to enable secure communication over HTTPS. Certificates should be properly installed and regularly updated.
- Encryption Protocols: API Gateways should support and enforce the use of strong encryption protocols, such as TLS 1.2 or higher, to protect against eavesdropping and tampering.
- Secure Cipher Suites: API Gateways should be configured to use secure cipher suites that provide strong encryption and forward secrecy.
API Key Management and Security Best Practices
API keys are commonly used for authentication and rate limiting. API Gateways should follow best practices for managing and securing API keys:
- Secure Generation and Distribution: API keys should be generated using secure random algorithms and distributed to clients over secure channels.
- API Key Rotation: API Gateways should support the ability to rotate API keys periodically to reduce the impact of key compromises.
- API Key Revocation: API Gateways should provide mechanisms to revoke or invalidate API keys in case of misuse or compromise.
- Secure Storage: API keys should be securely stored and protected, both on the client side and within the API Gateway.
Preventing Common Attacks
API Gateways should implement measures to prevent common security attacks. Some important functionalities are as follows:
- Input Validation: API Gateways should validate and sanitize incoming requests to prevent attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and parameter tampering.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling: API Gateways should enforce rate limits and throttling to prevent abuse, protect against denial-of-service attacks, and ensure fair usage of APIs.
- Security Headers: API Gateways should set appropriate security headers, such as X-XSS-Protection, X-Frame-Options, and Content-Security-Policy, to protect against common web vulnerabilities.
- Request and Response Validation: API Gateways should validate the structure and content of incoming requests and outgoing responses to ensure they adhere to the expected format and schema.
API Gateway Platforms and Tools
API Gateways have become an essential component of modern application architectures, providing a centralized layer for managing, securing, and exposing APIs.
Let's explore some of the popular API Gateway platforms available in the market.
Amazon API Gateway
Amazon API Gateway is a fully managed service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale.
It offers a comprehensive set of features and integrations:
- Seamless Integration with AWS Services: Amazon API Gateway integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like Lambda, EC2, and IAM for authentication and authorization. This integration allows developers to leverage the power of the AWS ecosystem for building and deploying APIs.
- Multi-Protocol Support: It supports multiple protocols, including REST, WebSocket, and HTTP, providing flexibility in designing and exposing APIs. This multi-protocol support enables developers to cater to different client requirements and use cases.
- Advanced Features: Amazon API Gateway offers features like request/response transformation, API versioning, and custom domain names. These features enhance the functionality and usability of APIs, making them more adaptable and user-friendly.
The diagram below shows a typical setup using the Amazon API Gateway:

Azure API Management
Azure API Management is a comprehensive platform for publishing, managing, and analyzing APIs within the Microsoft Azure ecosystem. It provides a rich set of capabilities for API management:
- Developer Portal: Azure API Management offers a developer portal for API documentation, testing, and onboarding. This portal facilitates developer engagement and adoption of APIs by providing a centralized hub for API exploration and interaction.
- API Versioning and Policy Enforcement: It supports API versioning, allowing multiple versions of an API to coexist. It also provides rate limiting, caching, and policy enforcement features to control and optimize API usage.
- Authentication and Authorization: Azure API Management integrates with Azure Active Directory for authentication and authorization, ensuring secure access to APIs. It supports various protocols like REST, SOAP, and WebSocket, catering to different API styles and requirements.
See the diagram below for understanding the capabilities of Azure API Management:

Google Cloud Endpoints
Google Cloud Endpoints is a fully managed API management platform provided by Google Cloud. It simplifies the development, deployment, and management of APIs running on Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Integration with GCP Services: Google Cloud Endpoints integrates seamlessly with other GCP services like Cloud Functions and Kubernetes Engine, allowing developers to build and deploy APIs using familiar GCP tools and services.
- API Versioning and Authentication: It provides features like API versioning and authentication/authorization using Google IAM (Identity and Access Management). These features ensure the proper management and security of APIs.
- Monitoring and Logging: Google Cloud Endpoints offers monitoring and logging capabilities, enabling developers to track API usage, and performance, and troubleshoot issues effectively. It supports both REST and gRPC APIs, catering to different API design preferences.
Kong
Kong is an open-source API Gateway and microservices management platform that provides a flexible and extensible solution for managing APIs:
- Plugin Architecture: Kong is built on top of NGINX and provides a plugin architecture for extending functionality. This plugin-based approach allows developers to customize and enhance the capabilities of the API Gateway based on their specific requirements.
- Multi-Protocol Support: It supports multiple protocols, including REST, gRPC, and GraphQL, making it suitable for various API styles and use cases. Kong can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, providing deployment flexibility.
- API Management Features: Kong offers features like API routing, authentication, rate limiting, caching, and request/response transformation. These features enable effective API management, security, and performance optimization.
Apigee
Apigee is a comprehensive API management platform owned by Google Cloud. It provides a wide range of features for API design, development, security, publishing, and analytics:
- Visual API Designer and Developer Portal: Apigee offers a visual API designer for creating and modifying APIs, as well as a developer portal for API documentation and testing.
- Authentication and Policy Enforcement: It supports various authentication mechanisms, rate limiting, caching, and policy enforcement. These features ensure the security and control of APIs, protecting them from unauthorized access and abuse.
- Advanced Analytics and Monitoring: Apigee provides advanced analytics and monitoring capabilities for tracking API usage and performance. These insights help in making data-driven decisions and optimizing API performance.
Summary
In this article, we’ve taken a detailed look at API Gateways and how they help build modern-day applications.
Let’s summarize the key learnings from the article:
- An API Gateway is a component that serves as the central entry point for all API requests in a system.
- Implementing an API Gateway provides several benefits such as centralized management, security, performance, and simplified client interaction.
- Some key features and functionalities provided by API Gateways are request routing, protocol transformation, API versioning, authentication, authorization, rate limiting and throttling, caching and response caching, and logging.
- API Gateways act as a reverse proxy, receiving client requests and forwarding them to the appropriate backend services.
- API Gateways play a vital role in integrating microservices and facilitating service discovery in a microservices architecture.
- API Gateways help secure and protect API communication by implementing various authentication mechanisms, enforcing authorization and access control policies, and following security best practices.
- Some popular API Gateway platforms are Amazon API Gateway, Azure API Management, Google Cloud Endpoints, Kong, and Apigee.
What does API Gateway Do?
Step 1 – The client sends an HTTP request to the API gateway.
Step 2 – The API gateway parses and validates the attributes in the HTTP request.
Step 3 – The API gateway performs allow-list/deny-list checks.
Step 4 – The API gateway talks to an identity provider for authentication and authorization.
Step 5 – The rate limiting rules are applied to the request. If it is over the limit, the request is rejected.
Steps 6 and 7 – Now that the request has passed basic checks, the API gateway finds the relevant service to route to by path matching.
Step 8 – The API gateway transforms the request into the appropriate protocol and sends it to backend microservices.
Steps 9-12: The API gateway can handle errors properly, and deals with faults if the error takes a longer time to recover (circuit break). It can also leverage ELK (Elastic-Logstash-Kibana) stack for logging and monitoring. We sometimes cache data in the API gateway.
Over to you: 1) What’s the difference between a load balancer and an API gateway? 2) Do we need to use different API gateways for PC, mobile and browser separately?